Access Denied
The greatest barrier to treating CNS disorders has been the inability of molecules to bypass the blood-brain barrier
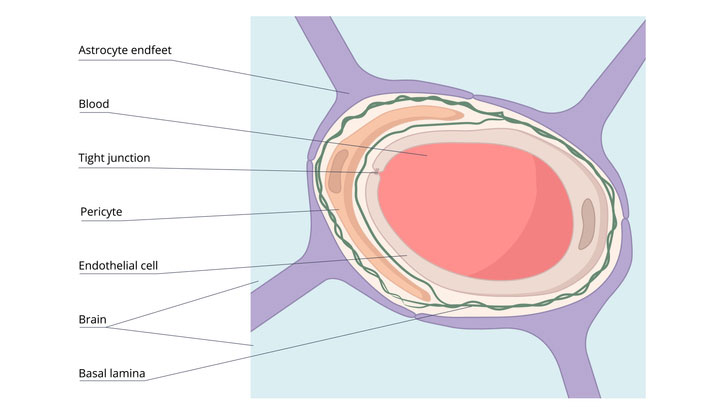
Blood Brain Barrier
The anatomical structure of the blood-brain barrier is formed by astrocyte endfeet, basal lamina, pericyte, endothelial cells, and tight junctions.
- The highly selective semipermeable border of cells shown above regulate the transfer of molecules between the circulatory system and the CNS
- This acts to effectively protect the brain from circulating pathogens and other potentially toxic substances
Most molecules can’t pass through the blood brain barrier in sufficient quantities:
Unmet need in brain tumors
Current therapies have a low response rates (RR) in recurrent tumors. These therapies are not targeted to tumor cells only resulting in severe toxicity
- Median Overall Survival of glioblastoma patients by therapy ranges between 3-20 months
- Recurrence typically occurs within months of surgery
- Survival after recurrence of about 8 months
- Average 5-year survival in glioblastoma is < 5%
- No clear improvement in prognosis for 20 years
- Secondary malignant brain tumors (brain metastases) account for about 200,000 new cases per year

Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) brain cancer – isometric view 3d illustration
Glioblastoma GBM, also referred to as a grade IV astrocytoma, is a fast-growing and aggressive brain tumor. It invades the nearby brain tissue, but generally does not spread to distant organs. GBMs can arise in the brain de novo or evolve from lower-grade astrocytoma.
Initial indication–Glioblastoma
- Glioblastoma is the most common and highly aggressive primary brain tumor from glial cells
- About 12,000 new cases in the US each year
- 30% of GBM patients have EGFRvIII mutation
- Standard of care (SOC): surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy
- Limited margins taken during tumor resection
- Results in tumor cells left behind that will continue to divide and grow
- BBB is intact around tumor tentacles.
- Poor delivery of therapeutics to tumor cells left behind after resection.
- No SOC after tumor recurrence
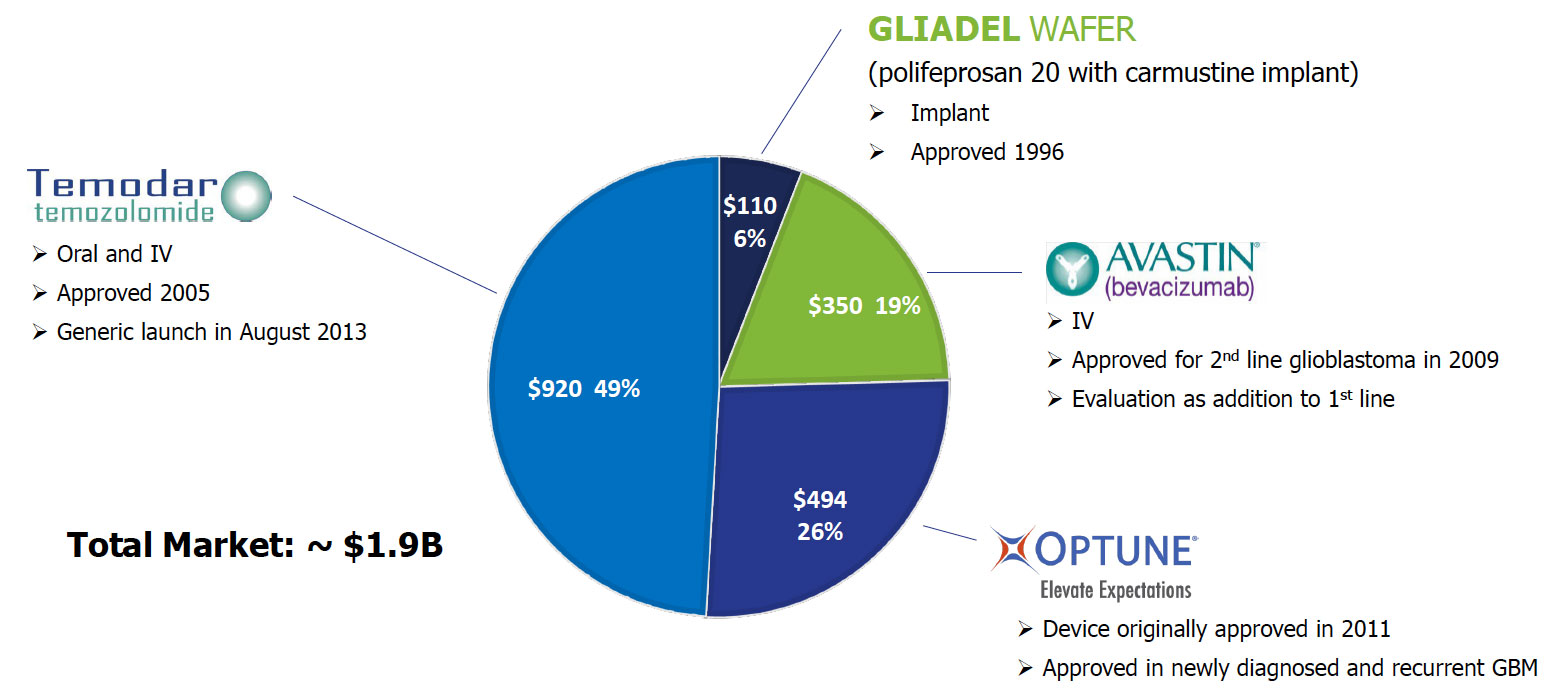
1.9b
Market size and current therapies
Several therapeutics are currently approved to treat glioblastoma representing a total market size of nearly $2 billion